Uterine Fibroids Treatment
Uterine Fibroids Treatment
Although uterine fibroids are non-cancerous, they can significantly affect a woman’s quality of life. These growths in the uterus can cause troublesome symptoms, such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and discomfort. While dealing with uterine fibroids can be challenging, there are several treatment options available that can help manage this condition and provide relief from associated symptoms.
What Is the Treatment for Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids treatment depends on several factors, including the size and location of the fibroids, the severity of symptoms, the patient's age, overall health, and personal preferences. Some of the common treatment options include:
Watchful waiting
A healthcare provider may recommend monitoring the fibroids without immediate intervention for women with asymptomatic fibroids or mild symptoms. Regular check-ups will help track any changes in size or symptoms.
Medications
Various medications are available to help manage the symptoms of fibroids or even shrink them temporarily. These include:
-
Hormonal medications like birth control pills, progestin-releasing intrauterine devices (IUDs), or gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists can help regulate the menstrual cycle and reduce heavy bleeding.
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
-
Tranexamic acid is a medication that can help reduce heavy menstrual bleeding.
Non-surgical procedures
Several myoma non-surgical treatments can help shrink or remove this growth, including:
-
Uterine artery embolization (UAE): This uterine myoma treatment involves the injection of tiny particles into the uterine arteries, which block the blood flow to the fibroids, resulting in their shrinkage.
-
Ultrasound-guided high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) uses high-intensity acoustic waves to heat and destroy fibroid tissues.
-
Radiofrequency ablation: A probe is inserted through the skin or via a laparoscope to deliver radiofrequency energy, which heats and destroys fibroid tissue.
Surgical procedures
In cases where fibroids cause significant symptoms or complications, surgical interventions, such as laparotomy (open surgery), laparoscopy, or robotic surgery, may be recommended:
-
Myomectomy: This surgery involves removing the fibroids while preserving the uterus, making it a suitable option for women who wish to maintain their fertility. However, it is possible for new fibroids to develop or any small remaining fibroid tissue to grow after myomectomy. Studies have reported varying recurrence rates, with some suggesting that up to 50% of women may experience fibroid recurrence within five years after the surgery.
-
Hysterectomy: This procedure involves removing the entire uterus and sometimes the ovaries. It is a definitive fibroids treatment but eliminates the possibility of future pregnancy.
Can Uterine Fibroids Be Treated Without Surgery?
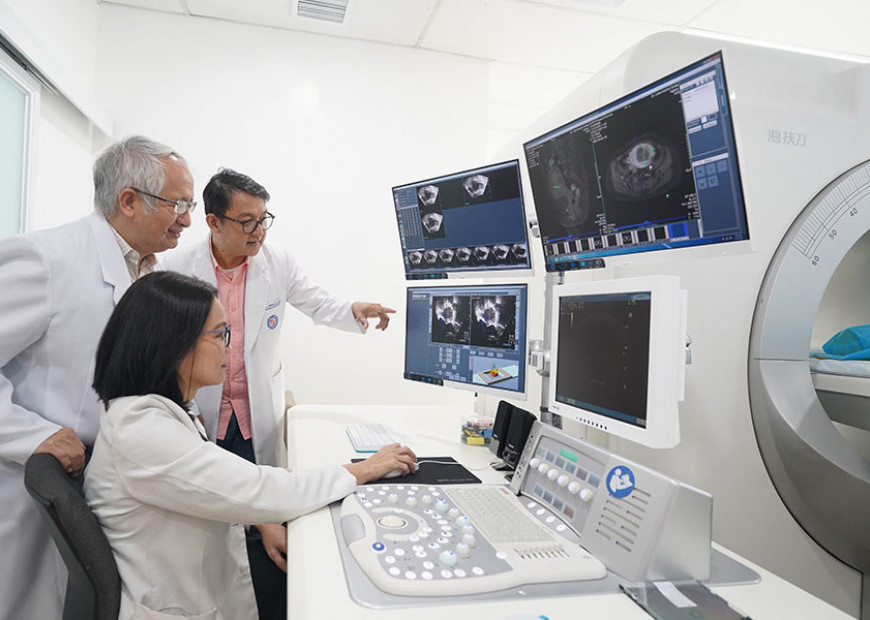
Women with uterine fibroids can be managed without surgery, depending on the size and location of the fibroids and their symptoms. Watchful waiting may be appropriate for some women, while others may benefit from new treatments for fibroids, such as medications or High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU), to shrink or destroy fibroid tissues. In order to find the best non-surgical approach, talk to your doctor about what treatment is best for you.
St. Luke's Medical Center in the Philippines introduces a cutting-edge facility at St. Luke's-Global City, specializing in High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU), an advanced non-surgical treatment using ultrasound beams to eliminate solid tumors without invasive surgery. The HIFU Unit offers transformative options for patients with uterine myoma, adenomyosis, and pancreatic and liver tumors, which is especially beneficial for those avoiding surgery or with physical constraints. Rigorous pre-procedure assessment and expert discussions ensure safety and efficacy; moreover, the procedure can be done on an outpatient basis, with swift recovery (3 to 4 days) and minimal discomfort.
This procedure offers the following advantages:
-
A non-surgical procedure for gynecological (myomas and adenomyosis), hepatic and pancreatic masses
-
Prevents complications related to surgical procedures
-
No surgical incision nor scarring
-
No blood loss
-
No damage to the surrounding normal tissues
-
Uses real-time ultrasound for a safe and precise ablation of uterine and hepatic tumors
-
Usually, a one-time treatment
-
An outpatient procedure for uterine myomas and adenomyosis
-
Requires only light sedation and analgesia for uterine myomas and adenomyosis
-
For infertility patients, they can try to get pregnant after 3 months.
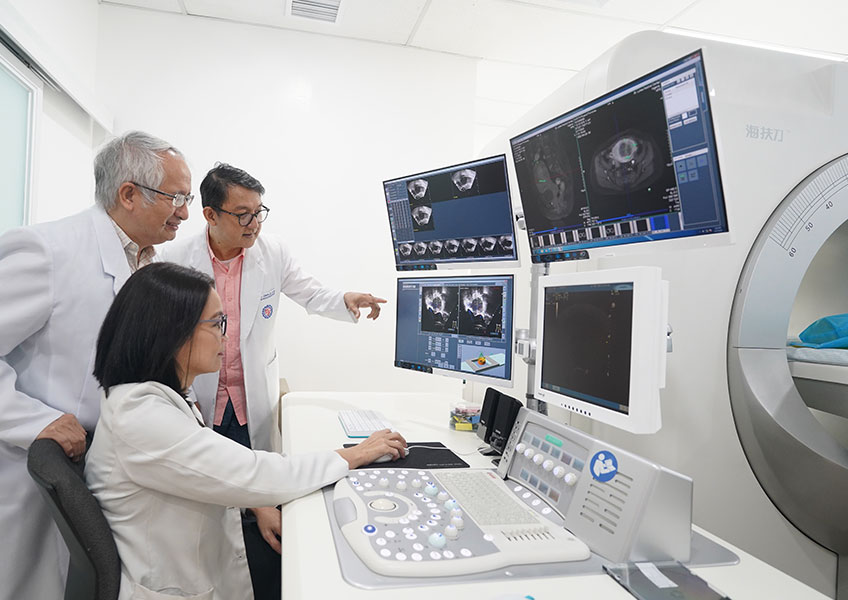
When Is Surgery Recommended for Uterine Fibroids?
Surgery may be recommended for uterine fibroids after considering various factors such as symptom severity, fibroid size and location, future fertility desires, and overall health. In general, patients undergo surgical interventions, such as open surgery or minimally invasive surgery, when symptomatic fibroids lead to significant pain or discomfort in the pelvic region, persistent bleeding, frequent urination, or difficulty emptying the bladder. It is also necessary when fibroids impact fertility, cause complications such as urinary retention, or if conservative approaches, including medication and non-invasive procedures, fail to alleviate symptoms.
Can Uterine Fibroids Come Back After Treatment?
Uterine fibroids can potentially come back after treatment. The likelihood of fibroid recurrence depends on the type of treatment received, the size and location of the original fibroids, and the patient’s hormonal status.
-
Myomectomy: This surgical procedure removes the fibroids but preserves the healthy tissues within the uterus. However, it is possible for new fibroids to develop or any small remaining fibroid tissue to grow after a myomectomy.
-
Non-surgical procedures: Conservative treatments for uterine myoma, such as uterine artery embolization (UAE) and radiofrequency ablation, may help shrink or destroy fibroids without surgery, but may not eliminate all fibroid tissue and recurrence is still possible.
Having a regular follow-up with your doctor is essential to monitor for any signs of fibroids recurrence.
Is Myoma/Uterine Fibroids and PCOS The Same?
While both myoma and PCOS are common in the reproductive age group, these two are distinct gynecological conditions with different underlying causes. Myoma refers to a benign growth in the uterus. In contrast, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder characterized by multiple small cysts in the ovaries, irregular menstrual cycles, and increased levels of male hormones (androgens).
As mentioned above, the most common uterine fibroids treatment in the Philippines is myomectomy, which removes the fibroids while preserving the healthy tissue of the uterus. This procedure is best for women who want to keep their uterus, particularly if they wish to become pregnant in the future. A myomectomy involves an incision in the lower abdomen to remove fibroids, followed by suturing of the uterine muscle.
Another option is hysterectomy, which involves removing the entire uterus. This is usually considered a last resort because of possible risks during the surgery. This is not suitable for patients who wish to become pregnant. However, it does offer a definitive resolution of fibroid symptoms.
Finally, laparoscopic procedures may be used to treat smaller fibroids or those located on the outer surface of the uterus. During this procedure, four tiny incisions are made in your abdomen so instruments can be inserted through them to remove the fibroid(s).
For women with uterine fibroids, St. Luke’s Medical Center offers comprehensive diagnosis and management. Our experienced team of OB/GYNs and specialists can help you find the best treatment for fibroids. Learn more about our services or schedule an appointment today by calling +632 8723 0101 or +632 8789 7700.





